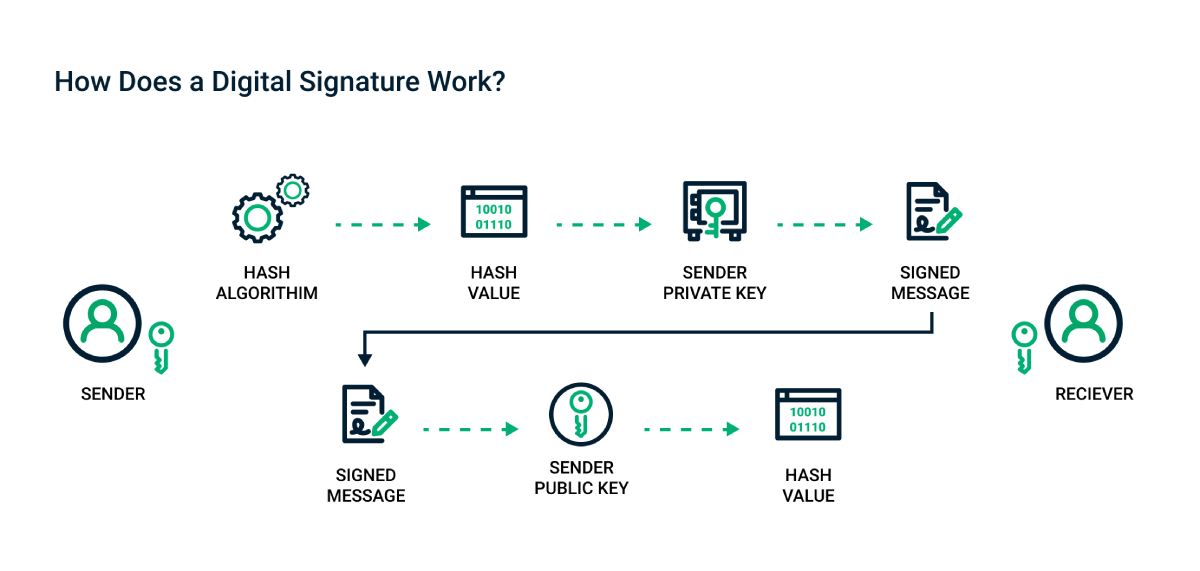
Digital signatures are two main definitions depending on the legal or technical concept being discuss.
Legally, the electronic signature is the digital equivalent of the handwritten signature and is intended to certify the wishes of the signer.
Technically, as specified in regulation 910/2014, known as eIDAS regulation, the electronic signature is a set of data in the electronic format annexed to other electronic data or logically associated with them that the signer uses to sign and that they collect in its set a series of basic functions among which are defined:
- Identification feature: uniquely identifies the signer
Authentication feature: guarantees the integrity of the signed document.
Non-repudiation characteristic: make sure the signer can’t repudiate/revoke the signed document. - In this feel, it is important to be aware that all digital signatures are digital signatures, however now not all digital signatures are virtual signatures.
- In wellknown, the electronic signature consists of all of the strategies to sign or validate an electronic file and become aware of someone.
On the opposite hand, the digital signature refers no longer only to the digital signature approach but to the complete manner this is included from the signature system to the validation of the signer’s signature. That is, it includes the act of signing itself and technical manner that permit it. For instance, to certify the identity of the signer, the date and time of signing, the certificates use, and that the signed report has now not been altering.
Table of Contents
Types Of Digital Signatures
The eIDAS regulation distinguishes three main types of digital signatures:
- Simple digital signature.
- Advanced digital signature.
- Qualified digital signature.
Essentially, these three types of signatures differ from each other by:
- security level
- Ability to guarantee the integrity of the document.
- Identification capacity of the signer.
Simple Or Basic Digital Signature (SES)
Taking into account the definition of the eIDAS regulation, all these signatures consist of a set of data in an electronic format that is logically add to other electronic data with which the signer uses to sign.
A simple digital signature could very well be a scan of a person’s handwritten signature. It is not because of its “simplicity” that it ceases to produce legal effects, admitting both as a method of signature and as evidence in the courts, although for this it will be necessary to use other elements to certify the authenticity of the signature.
Advanced Digital Signature (AES)
In the previous definition, the Advanced Digital Signature according to eIDAS is an electronic signature that also incorporates the following characteristics:
- Identification and liaison function of the signer.
- Document authentication function before any modification.
In short, it guarantees (i) the identity of the signer and (i) that the signed document has not been subsequently manipulating or modified.
Qualified Digital Signature (QES)
The qualified digital signature is a signature generat by a qualified signature creation device, base on trusted digital certificates that qualify for electronic signatures.
To create these companies, you need (i) a trusted electronic signature certificate and (ii) a qualified signature creation device, meeting both requirements set forth by the eIDAS regulations.
In this type of digital signature, the element of “Confidence in the electronic signature” technically comes into play. That is the digital certification by a third party (Trust Third Party or Certification Authority) of the identity. The validity, and link of the signature with its owner.
Digital Signatures And Confidentiality
The Digital Signature offers, in terms of Confidentiality and Data Protection. A field is full of possibilities and facilities for all types of applications. But more particularly when the Interested Parties can give their consent for the processing of their personal data.
Thanks to digital signature systems, the express, free, granular, and credible consent of the interest party can be obtain. Granting them a qualified level of security and truthfulness thanks to the inherent characteristics of digital signature systems (advanced or qualified in this regard). case ). Likewise, it allows the operation of obtaining consent to be more agile and automated. Allowing the express consent of the interested parties to be store practically automatically. Speeding up the processing of personal data related, for example, to the provision of services.
This increases the level of user experience and ultimately gives them an increase in the levels of privacy they enjoy. Minimizing all the processing and the signing process itself once digital signature systems are in use.
At Letslaw we have a team of highly specialized lawyers in Digital Law and New Technologies. If you have any questions or need more information, do not hesitate to contact us.